Effects of Coolant Type and Flow Velocity on Radiator Performance: A Comprehensive CFD Analysis
Keywords:
Automobile radiator, CFD, coolant fluids, water, ethylene glycol, liquid hydrogen, thermal performance.Abstract
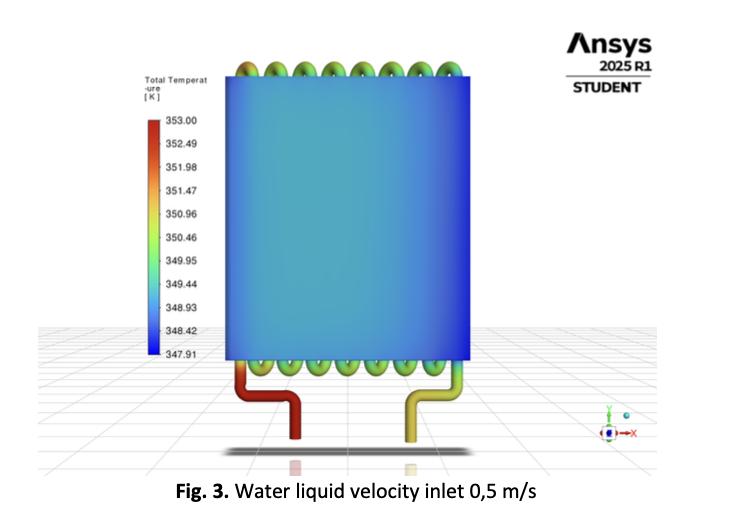
This study investigates the thermal performance of an automobile radiator utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to analyze three coolant types: water, ethylene glycol, and liquid hydrogen. Simulations were performed under steady-state conditions with a constant inlet temperature of 353 K and flow velocities of 0.5 m/s, 1.0 m/s, and 1.5 m/s. The analysis aimed to determine the effects of coolant type and flow velocity on temperature reduction and heat dissipation efficiency. Results indicate that liquid hydrogen outperformed ethylene glycol and water, achieving an average temperature reduction of 35.2% at 0.5 m/s, 32.5% at 1.0 m/s, and 30.1% at 1.5 m/s. In comparison, ethylene glycol provided reductions of 25.3%, 22.7%, and 19.8% under the same flow conditions, while water exhibited the lowest averages, with reductions of 15.4%, 13.5%, and 11.2%. The study also found that increasing flow velocity decreased per-pass temperature drop due to reduced residence time within the radiator channels. Notably, although per-pass efficiencies were lower at higher speeds, the overall heat removal rate increased, suggesting a trade-off between efficiency and effectiveness at varying flow rates. This research highlights the critical role of selecting appropriate coolant fluids and optimizing flow velocities in automotive thermal management systems. The findings provide essential insights for designing high-performance cooling systems and advocate for considering alternative coolants like liquid hydrogen in specialized applications.